What Is Session Initiation Protocol? The Essential Guide

Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is the often-unseen foundation of modern online communication. It powers voice and video calls, instant messages, and online conferences. Think of SIP as the orchestrator, managing all the different elements required for a smooth communication experience. Instead of using traditional phone lines, SIP uses your internet connection to transmit voice, video, and other data. This has significantly changed business communication, creating greater flexibility and substantial cost savings.
Understanding SIP: A Simple Analogy
Imagine ordering food at a restaurant. You don't communicate directly with the kitchen. You tell the waiter (SIP) your order. The waiter relays this to the kitchen and then brings your food. Similarly, SIP establishes and manages the connection between communication devices. It handles the initial setup, the ongoing communication, and the disconnection of the call or message. For example, during a VoIP call, SIP establishes the connection, manages call quality, and terminates the call when finished.
The Growth of SIP in the AE Region
SIP adoption is rapidly growing, especially in the Middle East and Africa. This growth is fueled by demand for cost-effective and adaptable communication solutions. The Middle East and Africa SIP trunking services market is projected to reach USD 1,551.30 million by the end of the forecast period, growing at a 10.3% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR). The on-premise segment currently leads this market, primarily due to the operational flexibility it offers large enterprises. More detailed statistics can be found here: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/middle-east-and-africa-sip-trunking-services-market
Key Advantages of SIP
SIP offers several key advantages for businesses in the AE region:
-
Cost Savings: SIP trunking significantly reduces communication costs compared to traditional phone lines.
-
Scalability: Businesses can easily scale their communication systems by adding or removing users and features with SIP.
-
Flexibility: SIP supports various communication methods, including voice, video, and messaging, all over a single IP network. This is particularly helpful for businesses with remote teams or those integrating communications with other business applications.
-
Improved Global Connectivity: SIP simplifies and improves international communication, reducing costs and improving call quality for global businesses.
SIP vs. VoIP: Clearing Up the Confusion
While the terms are often used interchangeably, SIP and VoIP are distinct. VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) refers to making voice calls over the internet. SIP is a specific protocol used to set up and manage those calls. Think of VoIP as the car, and SIP as the engine. SIP is one of several protocols used for VoIP, but its flexibility and features make it the most widely adopted. Understanding this distinction is crucial for business leaders modernizing their communications infrastructure.
How SIP Actually Works (Without the Headaches)
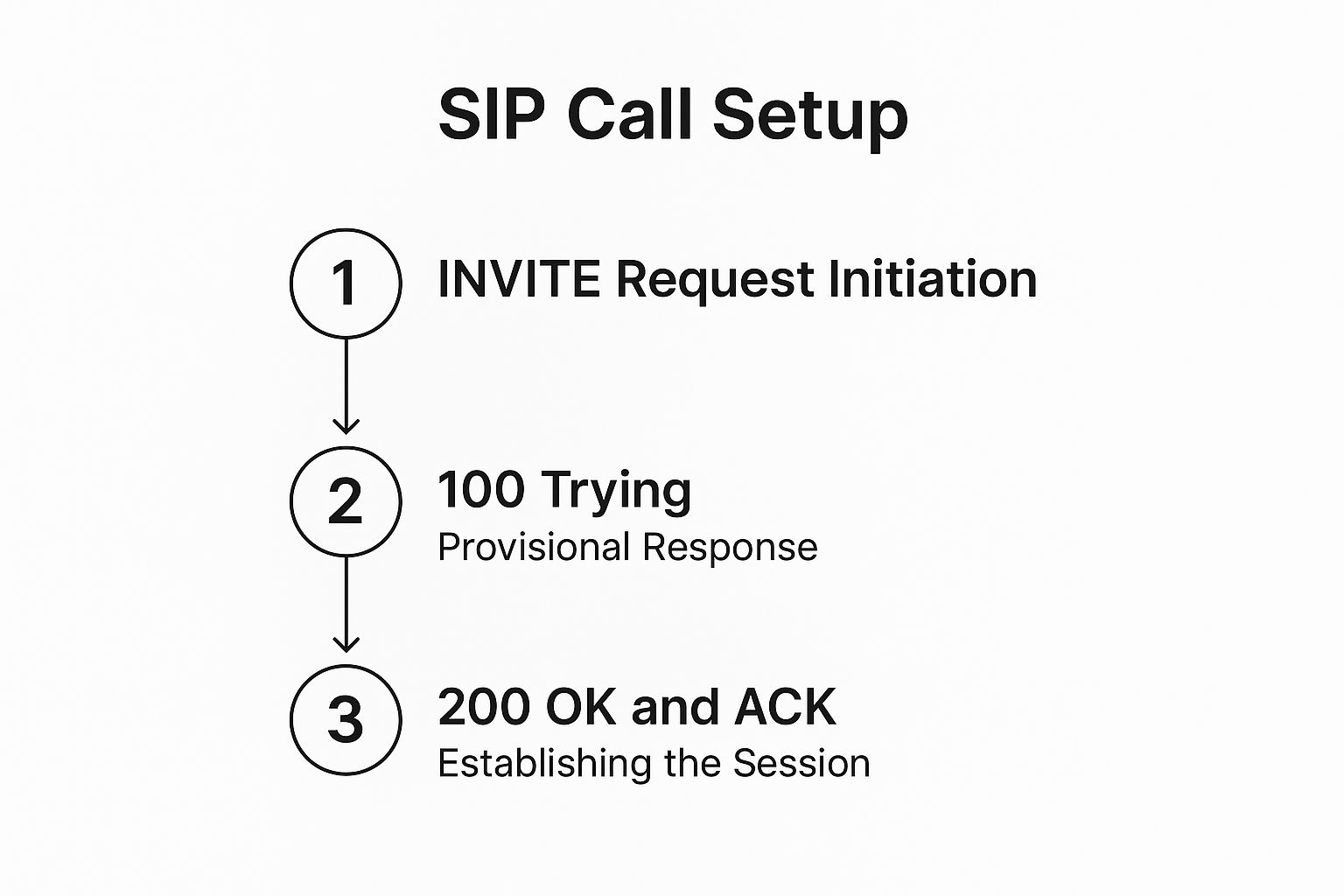
This infographic illustrates the basic process of a SIP call setup. It shows the journey from the initial request to the final connection in three key steps. The infographic demonstrates how SIP manages each stage, ensuring confirmation before proceeding. This process builds a reliable connection and facilitates clear communication.
Understanding the SIP Message Exchange
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) operates through a series of messages exchanged between devices. These messages act as instructions, guiding your phones on how to connect and communicate. The back-and-forth exchange is similar to email communication between servers. However, SIP utilizes its own distinct set of messages to handle real-time communication. Understanding these messages is fundamental to grasping how SIP truly functions.
Key SIP Messages and Their Roles
Several key SIP messages orchestrate a typical communication session. These messages work in concert to establish, manage, and terminate calls.
To illustrate this coordination, let's look at a simplified breakdown:
-
INVITE: The initial message initiating a communication session. Think of it as the digital equivalent of ringing a doorbell, signaling your intent to communicate.
-
TRYING: This message indicates that the call request is being processed. It's analogous to someone picking up the phone but not yet speaking.
-
RINGING: The recipient's device is ringing, indicating an incoming call and imminent connection.
-
OK: This signifies call acceptance. The connection between both parties is now established.
-
ACK: This acknowledgment confirms successful connection establishment. It’s the final handshake in the initial exchange.
-
BYE: This message terminates the call, concluding the communication session.
To further clarify the role of each message, let's look at a practical table summarizing their functions:
To help you grasp the function of each message, here's a quick reference table:
SIP Messages Decoded: What Each One Actually Does
A straightforward breakdown of the six essential SIP messages and how they work together to create seamless communications
| SIP Message | Primary Function | When It's Used | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| INVITE | Initiates a session | Start of a call | User A wants to call User B, so User A's phone sends an INVITE message. |
| TRYING | Indicates call request processing | After an INVITE is received | User B's phone receives the INVITE and sends TRYING while it processes the request. |
| RINGING | Signals that the recipient's device is ringing | While waiting for the recipient to answer | User B's phone rings, indicating to User A that the call is going through. |
| OK | Confirms call acceptance | When the recipient answers | User B answers the call, and their phone sends OK to User A's phone. |
| ACK | Acknowledges successful connection | After receiving OK | User A's phone receives OK and sends ACK to confirm the connection. |
| BYE | Terminates the call | End of a call | Either user hangs up, and their phone sends BYE to end the session. |
This table provides a clear summary of how each SIP message contributes to the overall call process. Understanding these individual roles offers a deeper insight into the mechanics of SIP.
SIP and Other Protocols: A Collaborative Effort
SIP doesn't operate in a vacuum. It works in conjunction with other protocols to provide a seamless communication experience. SIP manages the call setup and termination, while other protocols handle the actual transmission of voice and video data during the call. This collaborative approach ensures efficient management of the various aspects of communication. This inherent flexibility makes SIP highly adaptable for diverse communication requirements, particularly beneficial for businesses with varying needs. It enables the integration of voice, video, and messaging into a unified system.
SIP Trunking: Transform Your Business Communications

Many organizations are transitioning to SIP trunking, a technology that replaces traditional phone lines with internet-based connections using the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). This shift offers substantial benefits, especially for businesses in the Middle East and Africa looking for adaptable and cost-effective communication solutions.
Understanding the Advantages of SIP Trunking
SIP trunking offers compelling advantages over traditional phone systems. Cost savings are a primary driver. Businesses often report reductions of 30-50% compared to conventional systems.
These savings are achieved through lower call rates, the elimination of expensive hardware, and simplified infrastructure management. SIP trunking also allows businesses to instantly scale their communications up or down as needed, providing significant flexibility.
For companies with multiple office locations, SIP trunking offers a way to unify communications under one system, simplifying management and reducing complexity. This streamlined approach can lead to significant improvements in overall communication efficiency.
Benefits for Middle Eastern and African Businesses
The benefits of SIP trunking are particularly significant for businesses in the Middle East and Africa. Reduced international calling costs are a major advantage, facilitating better global connectivity and collaboration. This is especially important in a region with substantial international business activity.
Furthermore, SIP trunking helps overcome infrastructure limitations present in certain areas. It provides access to advanced communication features without requiring large on-site hardware investments. This allows businesses to compete globally, regardless of location.
Implementing SIP Trunking: Practical Considerations
Implementing SIP trunking requires careful planning. Businesses should evaluate their current communication needs and select a SIP provider that meets those requirements.
Factors to consider include call quality, reliability, security, and the level of support offered. Different implementation approaches exist for various business sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises with complex communication needs. Cloud Move, for example, offers SIP trunking solutions designed for businesses in the AE region. Learn more about SIP trunking solutions for your business.
Evaluating SIP Providers: Key Criteria
When choosing a SIP provider, several key factors should guide your decision. Look for providers with a proven track record of reliability and excellent call quality, particularly within the AE region.
Security is paramount; prioritize providers offering robust security features. Scalability is also crucial for growing businesses, so ensure the provider can accommodate future needs. Finally, excellent customer support is vital for troubleshooting any issues.
By carefully evaluating potential providers based on these criteria, businesses can ensure a smooth transition to SIP trunking and maximize its benefits. This proactive approach will allow businesses to improve communication and enhance operational efficiency.
Inside SIP's Architecture: Building Blocks That Matter
Having explored SIP trunking, let's now examine the core components that drive Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). A solid understanding of these fundamental elements is essential for comprehending how SIP provides reliable and scalable communication solutions.
Key Players in the SIP Ecosystem
Several vital components work together within the SIP architecture. Each element plays a distinct role in facilitating seamless communication.
-
User Agents (UA): Think of these as the individuals making and receiving calls. User agents are the endpoints—your IP phones, softphones, or video conferencing applications—that initiate and receive SIP communications. They serve as the interface between you and the SIP network.
-
Proxy Servers: These servers function much like a telephone operator, directing calls to the right destination. Proxy servers act as intermediaries, routing SIP messages between user agents. They also provide valuable services such as call forwarding and enhanced security features.
-
Registrar Servers: Imagine these servers as a digital address book for SIP devices. Registrar servers keep track of the locations of user agents, allowing them to be contacted via their SIP addresses (SIP URIs). Maintaining a directory of users and their current IP addresses is crucial for directing calls effectively.
-
Redirect Servers: Redirect servers inform user agents about alternative locations to reach a specific user. They can redirect calls based on pre-defined rules or user preferences, which is particularly useful for handling call forwarding or managing user mobility across different devices or servers.
SIP Addressing: Your Digital Communication Identity
SIP URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers) are the addresses used to identify users on a SIP network. Similar to email addresses, they typically follow the format sip:us**@****in.com. This standardized addressing scheme ensures SIP devices connect seamlessly, regardless of location.
The Power of Modular Design
One of SIP's greatest strengths is its modular design. This design allows for the easy addition or removal of different components, making SIP incredibly adaptable. This inherent flexibility simplifies integration with existing systems and adaptation to evolving business communication needs. SIP trunking leverages modern technology to optimize business communications, aligning with broader industry trends. For further insights into the future of customer service technology, see this article: Technology in Customer Service Trends. This adaptability makes SIP a future-proof solution for businesses.
To help clarify the different components within a SIP network, the following table summarizes their primary functions, deployment considerations, and business impact.
SIP Network Components: What You Need to Know
A clear comparison of crucial SIP network elements, their functions, and why they matter for your business communications
| Component | Primary Function | Deployment Considerations | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| User Agent (UA) | Initiates and receives SIP communications | Software or hardware-based | Enables direct communication between individuals |
| Proxy Server | Routes SIP messages; provides additional services like call forwarding and security | Centralized or distributed deployment | Improves call routing efficiency, enhances security, and increases scalability |
| Registrar Server | Tracks user agent locations via SIP URIs | Essential for accurate call routing | Ensures users are reachable by their SIP addresses |
| Redirect Server | Informs user agents of alternate contact locations | Useful for call forwarding and managing user mobility | Increases communication flexibility and streamlines call management |
Understanding these key roles and deployment considerations is vital for optimizing your SIP implementation and maximizing its potential benefits.
The Business Case for SIP: Beyond the Buzzwords

Switching to a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)-based communication system offers tangible benefits. This section explores the real-world advantages experienced by organizations in the AE region that have made the switch. Moving past the marketing jargon, we'll examine how SIP delivers cost savings, increased flexibility, and improved reliability.
Significant Cost Reductions: A Real-World Impact
One of the most compelling reasons for adopting SIP is the potential for significant cost savings. Many companies see a 30-60% decrease in their communication expenses.
This reduction comes from several key factors. SIP trunking eliminates the need for traditional phone lines and reduces hardware costs. Lower call costs, especially internationally, contribute further to these savings.
Additionally, SIP's streamlined infrastructure simplifies management and reduces ongoing maintenance. These combined savings can significantly impact a company's bottom line.
Communication Agility: Adapting to Change
SIP provides businesses with the agility to adapt to evolving communication needs. This adaptability is vital in today’s dynamic business environment.
Adding or removing users and features becomes a simple process, avoiding large capital expenditures. This scalability allows businesses to easily adjust their communication systems to accommodate growth or market changes.
This flexibility is particularly beneficial for businesses in the AE region, known for its rapidly shifting market dynamics. Understanding the architecture is crucial; learning more about data modeling with DAGs can be helpful.
Enhanced Reliability: Ensuring Business Continuity
SIP enhances communication reliability through features like automatic failover and geographic redundancy. In a system failure, calls are automatically rerouted to prevent disruptions.
This reliability is essential for businesses heavily reliant on communication for daily operations. Geographic redundancy strengthens this reliability by distributing resources across multiple locations.
This distribution minimizes the impact of regional outages, ensuring business continuity. This is particularly valuable in the AE region, where infrastructure limitations can present occasional challenges.
Addressing Regional Challenges in the Middle East and Africa
SIP is well-suited to address the specific telecommunication challenges faced by organizations in the Middle East and Africa. It overcomes infrastructure limitations by providing access to advanced features without requiring extensive on-site hardware.
Reduced international calling costs are a significant advantage for businesses in this region. Furthermore, SIP supports business growth by enabling scalable and flexible communication solutions that can adapt to the unique demands of the AE market.
Cloud Move, with its regional expertise, offers tailored SIP solutions designed to meet these specific challenges and empower businesses in the Middle East and Africa. Learn more about how Cloud Move can help your business: Learn More.
Implementing SIP: Challenges and Winning Strategies
Implementing a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) infrastructure can significantly enhance business communications. However, it’s important to acknowledge the potential challenges. This section explores common hurdles organizations in the AE region face during SIP deployment and offers practical strategies for a successful implementation. We'll cover everything from security concerns to quality of service issues, giving you the knowledge to navigate these complexities.
Security Concerns: Protecting Your SIP System
Security is paramount when implementing SIP. VoIP fraud and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are serious threats. These can disrupt communications and compromise sensitive information. Fortunately, several mitigation techniques can strengthen your SIP infrastructure.
These strategies include robust authentication mechanisms, encryption protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP), and deploying strong firewalls. Regular security audits and intrusion detection systems are also vital for proactive vulnerability management.
Quality of Service: Ensuring Clear Communication
High quality of service (QoS) is essential for a positive user experience. Choppy audio, dropped calls, and latency can hinder productivity and frustrate users. Proper bandwidth management, network prioritization for SIP traffic, and consistent performance monitoring are critical.
Implementing Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms on your network prioritizes voice and video traffic. This ensures a smooth and reliable communication experience. Consider using Virtual LAN (VLAN) tagging to separate SIP traffic from other data, further improving QoS.
Additionally, carefully assess your bandwidth needs. Choose an internet service provider (ISP) that can reliably deliver the required bandwidth, especially during peak hours. Thorough network testing before and after implementation helps identify and resolve potential QoS issues.
Compatibility Challenges: Integrating with Legacy Systems
Integrating SIP with existing legacy systems can be complex. Careful planning and proven integration approaches can minimize disruption. Assess the SIP compatibility of your current hardware and software. Upgrades or replacements may be necessary.
Phased deployments, where SIP is gradually introduced alongside existing systems, can smooth the transition. This approach also allows for thorough testing during each phase.
Regional Challenges in the Middle East and Africa
Organizations in the AE region face specific implementation challenges. Navigating regional regulations, addressing infrastructure limitations, and selecting appropriate providers require local expertise.
Engage with SIP providers familiar with the specific regulatory landscape. Look for providers with experience deploying solutions in the AE region. Choosing a provider with strong local support and infrastructure can simplify implementation.
Implementation Roadmap: A Step-by-Step Guide
A structured approach is crucial for successful SIP implementation. The following roadmap provides a step-by-step guide based on best practices:
-
Assessment: Evaluate current communication needs and infrastructure.
-
Planning: Develop a detailed implementation plan, including budget, timeline, and resource allocation.
-
Provider Selection: Choose a reputable SIP provider with AE region experience.
-
Deployment: Implement the SIP solution as planned.
-
Testing: Thoroughly test the system for functionality and QoS.
-
Training: Train users on the new system.
-
Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor performance and adjust as needed.
By proactively addressing these challenges and following a structured roadmap, businesses in the AE region can unlock SIP's full potential and transform their communications. Ready to experience the benefits of a robust and reliable SIP solution tailored to the AE region? Cloud Move offers expert consultancy and free demos to optimize your communication strategy. Learn more about Cloud Move's SIP solutions.




